Steps to grow your KVM VM/Container’s partition after extending root OS size or extending ext2/3/4 and XFS root partition without LVM at runtime. These steps will work on most Debian/Ubuntu and CentOS based systems.
Requirements
1) Root access to the System/VM/Container.
2) Extended root OS Size (for KVM VM/Containers only)
Steps
> First, log in to the root user of the System/VM/Container after root OS Size is increased.
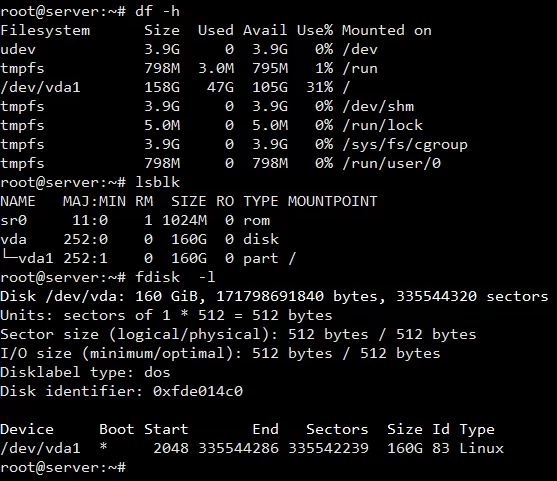
> Then check the partition details of the system using lsblk and fdisk -l commands as the image below.
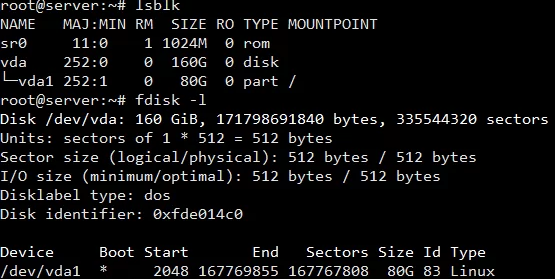
> Below given image shows that the OS partition size vda is 160GB in total but the vda1 system root / the total size is 80GB currently. You can see more details by using df -h the command.
> To enlarge the partition you need to install cloud utils package and run growpartthe command to increase the partition. The growpart is a Linux command-line tool used to extend a partition in a partition table to fill available space. Use the following command to install cloud utils package.
On Ubuntu / Debian system:
sudo apt -y install cloud-guest-utils gdisk
For CentOS System:
sudo yum -y install cloud-utils-growpart gdisk
> Use growpart to extend the partition vda1.
growpart /dev/vda 1
Here /dev/vda is the main OS Partition and 1 is sub-partition number 1 which indicates you can extend /dev/vda1 partition by running the above command.
![]()
> Then check the partitions details using lsblk command. It should show sub-partition number 1 extended to 160GB.
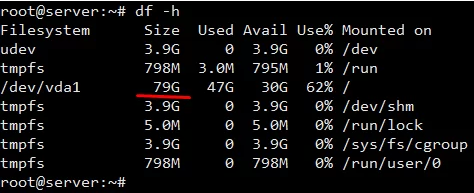
> Now, check what type of partition your system is using with the help of df -Th command.
> Now, you can resize / partition to fill all space in /dev/vda1 partition using the resize2fs for ext partition command as below
.resize2fs /dev/vda1
Note: If your filesystem is XFS, it can be grown while mounted using the xfs_growfs command as below.
xfs_growfs -d /dev/vda1
> You can confirm the new size by running the commands df -h, lsblk and fdisk -l. You can see now vda1 partition is 160GB in total size.